
Setting Up a Server Environment with PHP 8.2
In today’s blog, we’ll walk through setting up a server environment for PHP applications, with the latest PHP version (8.2), on an Ubuntu system. We will be using the Apache web server and MySQL for the database. The instructions provided in this blog should also work for other distributions of Linux. Let’s get started!
- System Update
First things first, let’s make sure that our system is up to date. You can do so by running the following commands:
sudo su
sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get -y upgrade
- Installing Required Software
We’re going to need some software utilities for our setup. Run the following commands to install them:
sudo apt-get -y install software-properties-common python-software-properties
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:dawidd0811/neofetch
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:ondrej/php
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:keithw/mosh
sudo apt-get -y update
- Installing Apache
Next, let’s install the Apache web server with the following command:
sudo apt-get -y install apache2
- Installing MySQL
sudo apt-get -y install mysql-server
- Installing PHP 8.2
We are ready to install PHP 8.2. Let’s add the repository for PHP and then install PHP with the required extensions:
sudo apt-get -y install php8.2 php8.2-dev php8.2-cli php8.2-common php8.2-curl php8.2-gd php8.2-json php8.2-mbstring php8.2-intl php8.2-mysql php8.2-xml php8.2-zip libphp8.2 libapache2-mod-php8.2 libmcrypt-dev php8.2-redis php8.2-mongodb
Now, it’s time to install some additional tools:
sudo apt-get -y install curl zip unzip rar unrar mosh ncdu neofetch net-tools wget openssh-server ssh libcurl4-openssl-dev libssl-dev
- Configuring Apache and PHP
Next, let’s configure our Apache web server. First, we’ll back up the original Apache configuration file:
sudo cp /etc/apache2/apache2.conf /etc/apache2/apache2.conf.bkp
Now let’s edit the Apache configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Paste the following in the file:
<IfModule mpm_prefork_module>
StartServers 4
MinSpareServers 20
MaxSpareServers 40
MaxClients 200
MaxRequestsPerChild 4500
</IfModule>
<Directory /var/www/html/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
Save the changes and close the file. Next, enable Apache modules and restart the server:
sudo a2enmod rewrite headers
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Now, we are ready to set up a VirtualHost for our domain:
sudo a2dissite *default
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/domain.com/{public_html,logs,backups}
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/domain.com.conf
Paste the following configuration in the domain.com.conf file:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin [email protected]
ServerName domain.com
ServerAlias www.domain.com
DirectoryIndex index.html index.php
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/domain.com/public_html
LogLevel warn
ErrorLog /var/www/html/domain.com/logs/error.log
CustomLog /var/www/html/domain.com/logs/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Save and close the file. Enable the site and reload the Apache server:
sudo a2ensite domain.com.conf
sudo systemctl reload apache2
- Securing MySQL
Now it’s time to secure our MySQL installation:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
You’ll be asked a series of questions. Respond as follows:
- VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN: `n`
- Change the password for root: `n`
- Remove anonymous users: `y`
- Disallow root login remotely: `y`
- Remove test database and access to it: `y`
- Reload privilege tables now: `y`
Configuring MySQL User and Bind-Address
mysql -u root -p
Inside the MySQL shell, create a new user and grant all privileges:
CREATE USER 'username'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'strongPassword';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO 'username'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Edit the MySQL configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/mysql/my.cnf
Add these lines to the file:
[mysqld]
bind-address=0.0.0.0
sql_mode=''
Save and close the file.
Set your time zone (Optional):
timedatectl
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Kolkata
Restart MySQL and set permissions for the HTML directory:
sudo service mysql restart
sudo chmod 775 -R /var/www/html/
sudo chown -R ubuntu:www-data /var/www/html/*
Now, update your .bashrc file (Optional):
here you can add alias for different commands for example
echo 'HISTTIMEFORMAT="%y-%m-%d %T "' >> ~/.bashrc
echo "alias www='cd /var/www/html'" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "alias apl='sudo tail -f /var/log/apache2/error.log'" >> ~/.bashrc
echo "alias upd='sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y upgrade && sudo apt-get -y autoremove && sudo apt-get -y autoclean'" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
- Security Setup
sudo apt-get -y install ufw
sudo ufw allow 22,80,443,3306,8080,8443,9090,9933/tcp
sudo ufw allow 60000:61000/udp
sudo ufw enable
We will also set up Fail2Ban for some extra security:
sudo apt-get -y install fail2
If you are using multiple php version then you can switch between them via below commands
sudo a2dismod php7.2
sudo a2enmod php8.2
sudo service apache2 restart
php -v
- Tags:
- #Laravel

Author: Manish Kumar
I've been working with PHP for over 11 years and focusing on Laravel for the last 6 years. During this time, I've taken part in big projects and gotten to know tools like Laravel Livewire really well. Besides working on projects, I enjoy writing about Laravel on LinkedIn and Medium to share what I've learned. I'm always looking to learn more and share my knowledge with others. Right now, I'm diving into new areas like using Docker to make web apps run better and exploring how to build them using microservices. My goal is to keep learning and help others do the same in the world of web development.
Recent Posts

How to Generate a Package in Laravel and Why It's Important
Manish Kumar
22 Jul 2024

Writing Clean Code in Laravel: Principles and Tools
Manish Kumar
15 Jun 2024

Basic Useful Commands for Developers
Manish Kumar
12 Jun 2024
Exploring Key Design Patterns in Software Development
Manish Kumar
29 May 2024
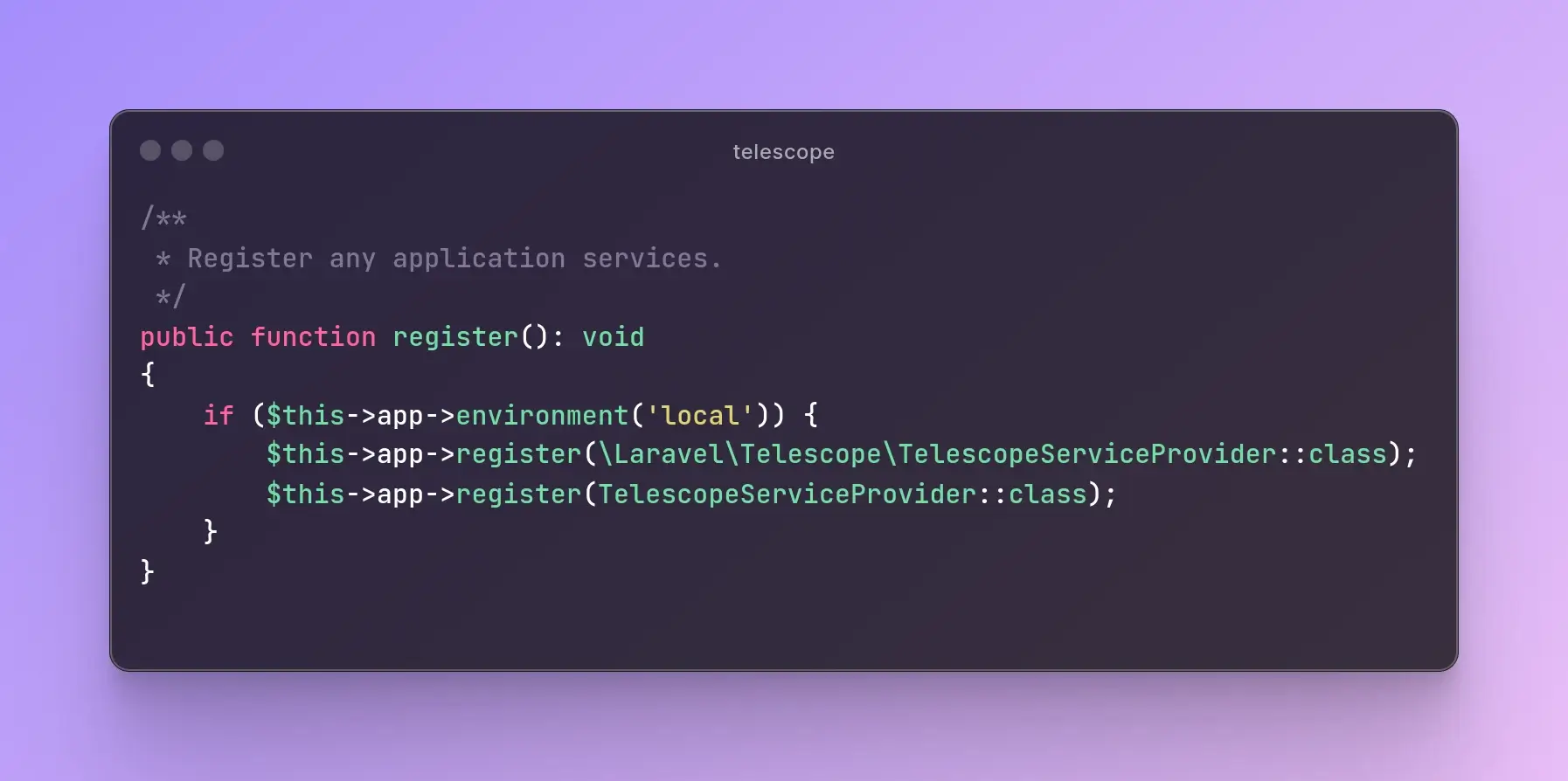
Laravel Telescope: Debugging Made Easy (Part - 2)
Sonu Singh
25 Apr 2024

Subscribe to Newsletter
Provide your email to get email notification when we launch new products or publish new articles